What defines a smart city?
A city where residents, infrastructure, public transportation, city administration, and local governing bodies all utilize technology and data-driven solutions to enhance the quality of life, practice responsible resource consumption, and foster economic prosperity. The ultimate goal of a smart city is to improve the well-being of its citizens by employing the Internet of Things to optimize infrastructure and services.
We envision a smart city as a future that offers an improved standard of living and promotes sustainable use of utilities, energy, and natural resources. With the advent of modern technologies in the market, people are elevating their quality of life. This transformation is particularly prominent in the real estate sector, where builders are either constructing smart properties or transforming existing houses and offices into smart living and working spaces. This is achieved by incorporating internet-connected devices and enabling automation in systems and appliances, resulting in spaces that exude a super chic and modern aesthetic.
A smart city is often described as city automation, signifying that individuals within the city or society have security, advanced surveillance systems, comfort, convenience, smart devices at home, intelligent parking solutions, health monitoring systems, integrated sensors in public spaces, waste reduction measures, and cashless transactions—all of which can be controlled through smartphones or networked devices.
While developing a smart society, it is crucial to prioritize data privacy, ensure that benefits are accessible to all residents, minimize risks, perform timely maintenance, and encourage community involvement and feedback
Key features of a smart city encompass
Smart Infrastructure:
Integration of smart devices and technologies in areas such as transportation, energy, water supply, and waste management to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT):
Integration of sensors and communication networks to collect and analyze data for efficient utility management.
Sustainability:
Implementation of eco-friendly practices and technologies to mitigate environmental impact, including solar energy-efficient buildings, renewable energy sources, and waste reduction.
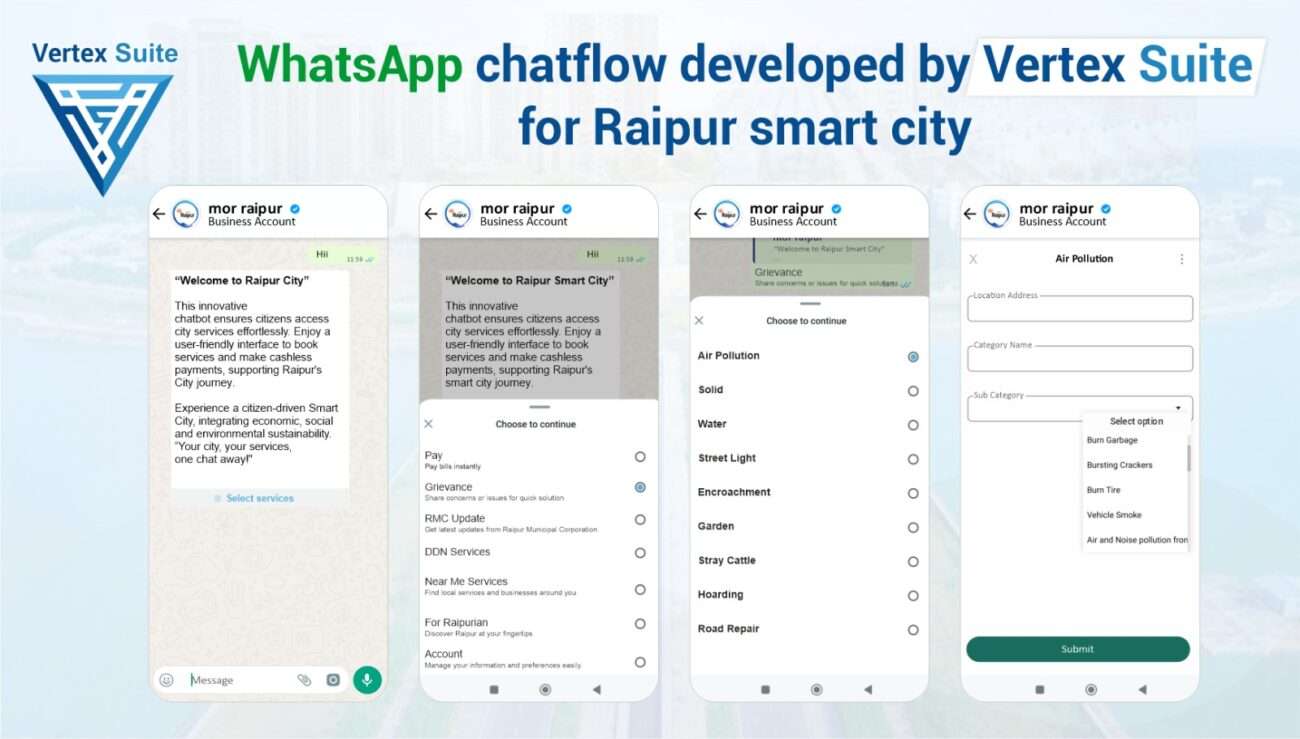
E-Governance:
Utilizing digital platforms to enhance government services, engage senior citizens, and provide interactive platforms for overall governance.
Advanced Education Systems:
Implementation of smart classrooms, digital learning platforms, and technologies to enrich the educational experience and make learning more interactive.
Safety and Security:
Deployment of advanced technologies for public safety, surveillance, and emergency response to ensure the well-being of citizens.
Quality of Life:
Emphasis on improving the overall quality of life for citizens through initiatives addressing healthcare, education, cultural opportunities, and community engagement.
Community Engagement:
Implementation of digital cultural platforms, community events, and social networks to facilitate communication and provide entertainment among residents.
Efficient Transportation:
Integration of smart public transportation systems, real-time traffic management, and intelligent parking solutions to reduce congestion and enhance overall transportation efficiency.
Waste Management Solutions:
Implementation of smart waste bins, recycling initiatives, and technology-driven approaches to effectively reduce and manage waste.
How does smart home technology work?


Smart home technology involves the use of devices and systems connected to a network, enabling monitoring, control, and remote automation. Let's explore a general overview of how smart home technology operates.
Devices and Sensors:
Smart home technology encompasses a diverse array of devices, including smart thermostats, lights, doorbells, cameras, locks, appliances, and more. These devices are equipped with sensors, processors, and communication modules that enable remote control.
Connectivity:
Nearly all smart home devices are connected to a home network, usually through Wi-Fi or other wireless protocols. This connectivity facilitates communication between devices and with a central control hub.
Central Control Hub:
Many smart homes feature a central control hub or a smart home platform that acts as the system's core, such as smart speakers like Amazon Echo or Google Home.
Mobile Apps and Interfaces:
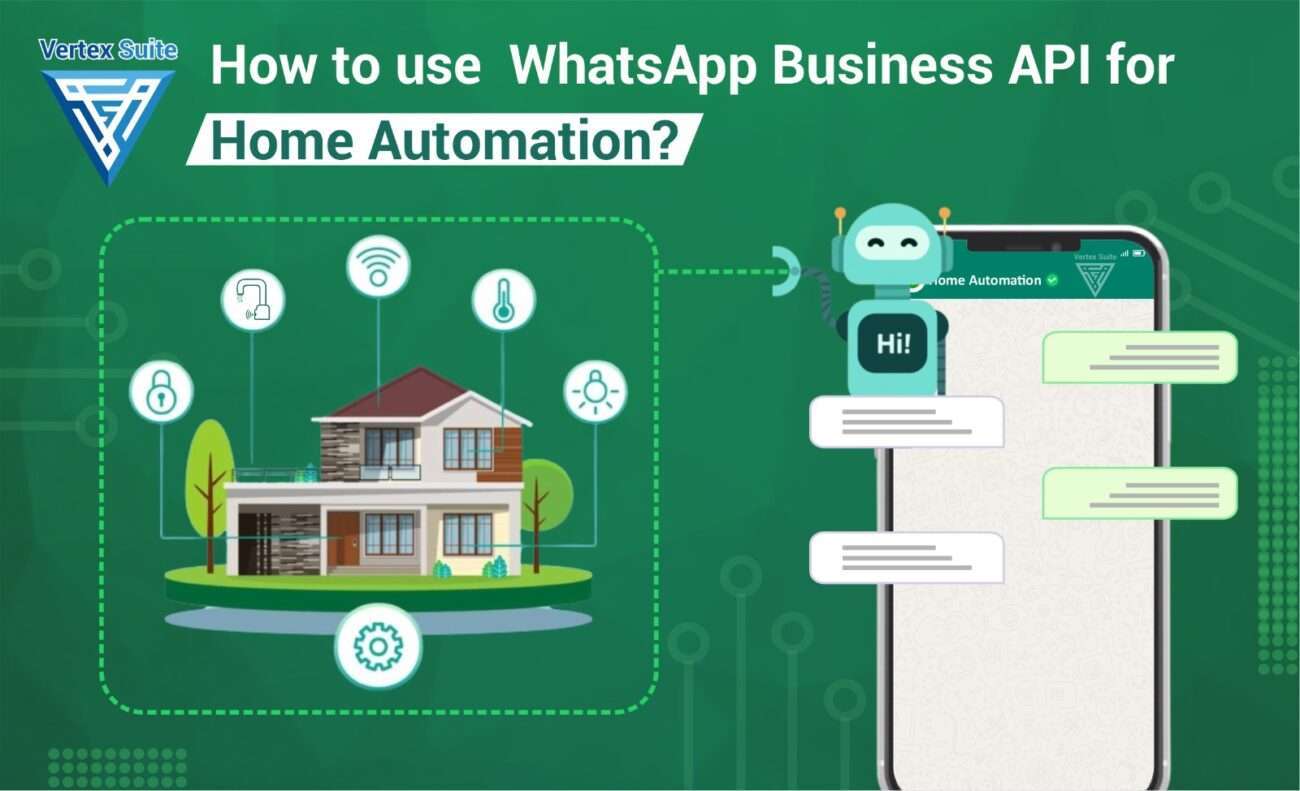
Users can control and monitor smart home devices through mobile interfaces without the need for additional apps, for example, through messaging platforms like WhatsApp. The advent of IoT on WhatsApp Business API enables access to all devices through a single messaging app, eliminating the necessity for multiple installations.
Home Automation:
A key feature of smart home technology is automation. For instance, lights can automatically turn on when motion is detected, or thermostats can adjust temperatures at specific times.
Voice Control:
Many smart home systems support voice control, such as Amazon's Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple's Siri. Users can issue voice commands to control devices, set scenes, or inquire about the status of their smart home.
Cloud Integration:
Smart home platforms often utilize cloud services for additional functionality and remote access. Cloud integration enables users to control their smart home devices even when they are away from home.
Security and Encryption:
Security is a critical aspect of smart home technology. Devices and communication channels are typically secured using encryption protocols to safeguard user data and prevent unauthorized access.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Some advanced smart home systems incorporate AI to learn user preferences over time and optimize device settings.
Energy Efficiency:
Smart home technology contributes to energy efficiency by allowing users to monitor and control energy-consuming devices. For example, smart thermostats can optimize heating and cooling based on occupancy and external weather conditions.